Electronic waste doesn’t just disappear after it’s recycled. Once devices are broken down, their materials, including plastics, metals, and glass, are processed and reused in real products that show up all around us. Here are five common examples of what recycled electronics often become.
1) New electronics housings and plastic components
One of the most direct reuse paths for e-waste is closed-loop recycled plastic. Plastic recovered from old electronics is cleaned, processed, and molded into new casings for monitors, desktops, and laptops. Dell is a well-known example, openly documenting how plastic from recycled electronics is reused in new products.
Learn more about closed-loop electronics plastics here:
https://www.dell.com/en-us/blog/circular-design-gives-e-waste-a-second-life/
https://eom.org/knowledge-hub-content/dell
2) Heat sinks and aluminum components
Aluminum is one of the most valuable materials recovered from electronic waste. Old electronics contain aluminum in frames, housings, and cooling systems, and once recycled, that aluminum is frequently reused in heat sinks and other thermal components.
Because aluminum can be recycled repeatedly with minimal quality loss, it’s a staple material in electronics manufacturing.
Example of recycled aluminum heat sink use:
https://www.ennergroup.com/news/recycled-aluminum-heatsink.html
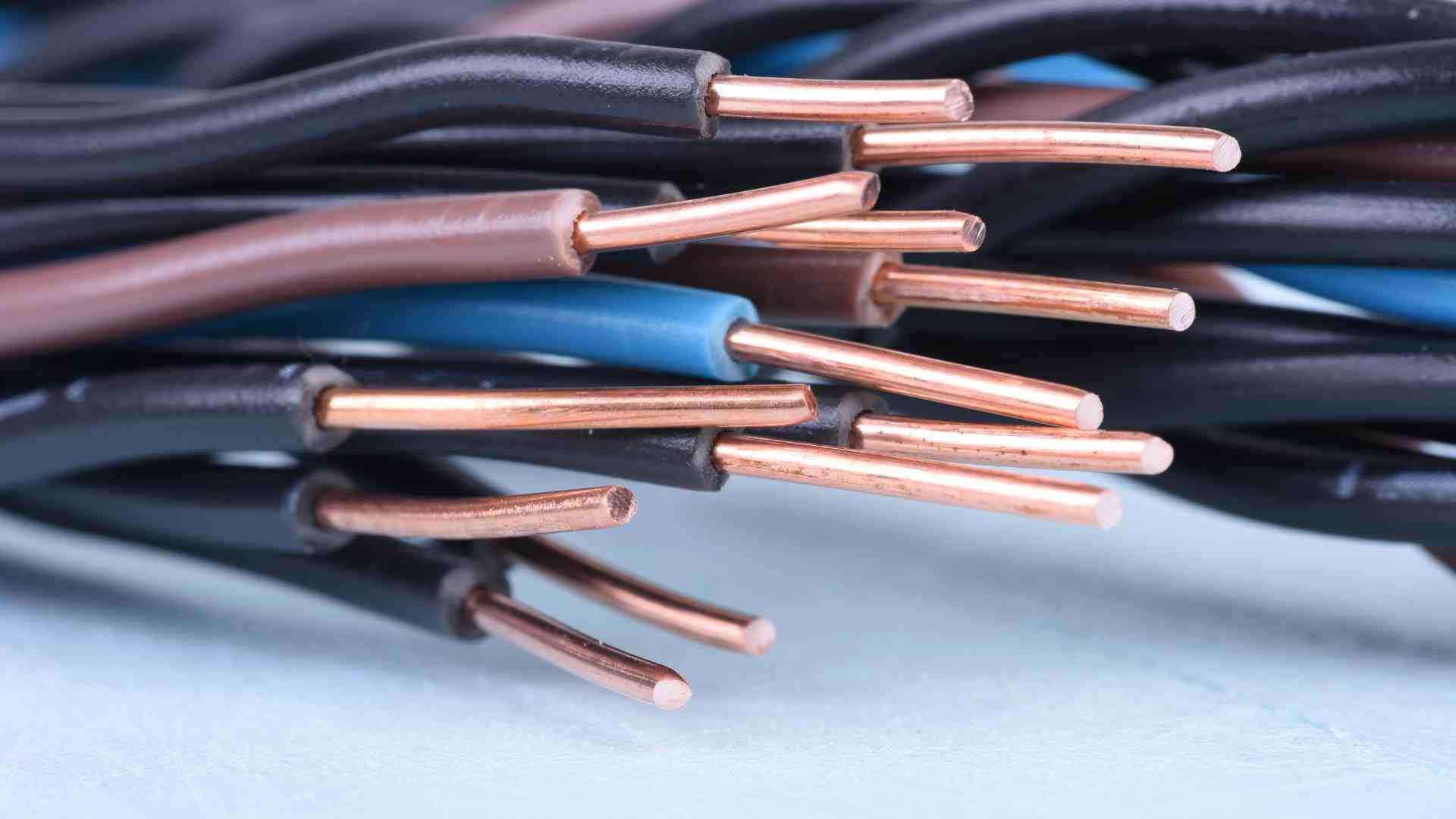
3) Copper reused for wiring, construction, and energy systems
Electronics are packed with copper—wires, circuit boards, and internal components all contain it. When recovered through e-waste recycling, copper is commonly reused in new wiring, building materials, and renewable energy infrastructure.
This isn’t a niche practice. Industrial recyclers now operate large-scale facilities dedicated to extracting high-purity copper from electronic waste.
Overview of copper reuse from e-waste:
Industrial example (Reuters):
4) Recycled glass used in new manufacturing
Screens and displays generate significant amounts of glass waste. When properly recycled, that glass can be reused as a raw material in manufacturing. Some electronics companies now highlight recycled glass as part of their sustainability and energy-reduction efforts.
Dell, for example, has discussed using recycled glass to lower manufacturing energy demands while diverting waste from landfills.
More on recycled glass in electronics:
https://www.dell.com/en-us/lp/dt/sustainable-devices
5) Jewelry and accessories made from recovered e-waste materials
Not all recycled electronics go back into factories. Some recovered materials—especially metals—are repurposed into jewelry and accessories. Artists and small brands have turned circuit boards, copper, and other reclaimed materials into wearable pieces.
This reuse pathway has even made its way into mainstream media.
Overview of repurposed e-waste materials:
https://firstamerica.com/e-waste-recycling-process/
CNBC feature on e-waste jewelry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GxZysJL5VJc
What Recycle IT is doing to help
Recycle IT is doing its part to keep electronic waste out of landfills by offering free commercial electronics recycling for Utah businesses. Instead of letting outdated or broken tech pile up, local companies can responsibly recycle their electronics at no cost while ensuring materials are properly processed and reused. Scheduling is simple, and businesses can book a pickup or drop-off in just a few minutes using this link.
Aluminum Heat Sink:

Copper Wire:
Glass Recycling:

